How To Fix Windows Update Issues
Windows update can cause several issues, often leaving you with a cryptic error message such as 0x8024402c, 80070643, 8024800A or many others. Alternatively, you may also get an error like "Windows update cannot check for updates because the service is not running" . This article will go through how to troubleshoot Windows Update issues as a whole.Instructions for various specific issues such as those shown above can also be found on this site (just use the search feature to locate them).
Windows Update Fix It Tool
This tool is a great starting point for troubleshooting Windows Update and is highly successful in resolving a variety of issues. The Tool can be downloaded here:
http://support.microsoft.com/mats/windows_update/ . At the time of writing there was no Windows 8 64 Bit version of this tool, hopefully Microsoft will make a version available in the near future.
Windows Update Log
For Those who wish to do further troubleshooting or if the above tools do not solve your issue, the Windows Update Log is a great place to start looking for clues as to what is going on. to access the log open a Run Command and type (or just copy from this blog) %Windir%\windowsupdate.log and press Enter. I have included a snippet from a log below:.
In this case, the log is displaying that error 0x800f0902 has occurred where Windows was unable to download updates. This is a fantastic starting point for further troubleshooting of issues that are occurring.
Windows Services
There are three main services involved with Windows Update, the Windows Update Service, Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS ) and the Workstation Service. If any of these are not started and running, Windows will be unable to apply updates.
To access the Windows Services open a
Run Windows (
Windows Key + R) and enter
services.msc . This will open a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) showing Running Services.
For each of the above services check the following:
- Scroll down till you find the service (in this case Background Intelligent Update Service). as seen in the picture, the status should be Running and the Startup Type should be :
- Automatic (Delayed Start) for the BITS service
- Automatic for the Workstation Service
- Manual (Trigger Start) for the Windows Update Service - (note that on some Windows 7 Systems it may also be set to Automatic Start)
- If the services are shut down, or not set to the appropriate start up type:
- Double Click on the Service. This will open the Properties Window for the service
- Change the Startup Type to the correct mode and /or click start to start the service
- If the service will not start, then a good thing to do is run the above Fix It Tool or System Update Readiness Tool and see the results. failing that, consult the Windows Update log as also shown above.
Deleting Windows Update File Locations
If you have an update that will not successfully install (e.g. it repeatedly tries to install but fails when shutting down) or further investigation has suggested, it may be necessary to manually delete the files and folders containing Windows Update data and database. Please ensure that you have backed up any data or created a restore point before deleting any files
Note that before doing this you may need to stop with Windows Update Service. - see above for instructions on how to locate the service. once found double click the service to expose the properties window and choose stop. After you can either reboot to start the service or double click and choose start
The Windows Update download location can be found at
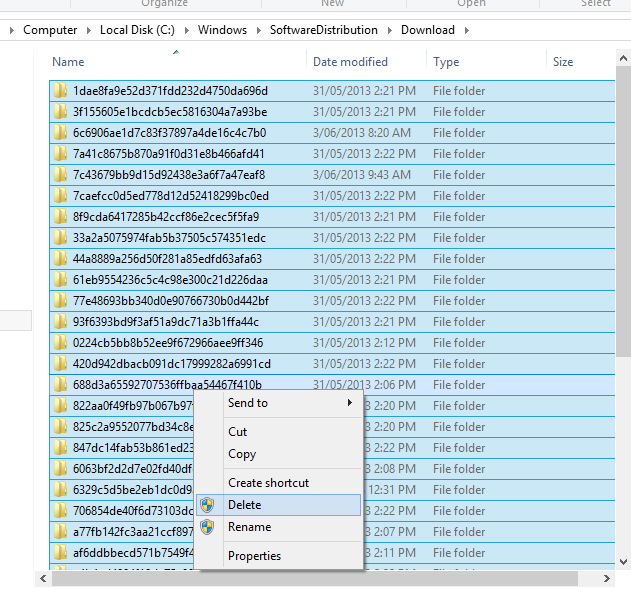
C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download . This is the repository where windows stores downloaded updates.
Its normally OK to delete these files as they are just the installers, not the actual applied updates. To delete these , click on the window, and press
Control and A . This will highlight all the items in the screen.
Right Click and choose
Delete. answer
YES to any verifcation prompts.
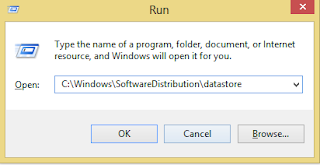
The Windows Update Download location is found at
C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\datastore .
This is the actual location of the Windows Update Database. if this database is corrupted then it may be easiest to delete it. Windows should create a new database automatically. To delete the database, open the location above click on the window, and press
Control and A . This will highlight all the items in the screen.
Right Click and choose
Delete. answer
YES to any verification prompts.
Uninstall Windows Updates
Occasionally you will installa n update that may not play nice with your system due to incompatibility with other installed programs, a failed install or occasionally an update that is not functioning as Microsoft intended. to remove these updates:
- Open Control Panel
- In Windows 7 / Vista / 2008 go to Start -> Control Panel
- In Windows 8, or Server 2012 go to the Start Screen and type Control Panel. this will bing up the control Panel Icon. Choose this Icon
- Select to view by Small Icons (Optional) then choose Programs and Features
- in the left hand corner, select View Installed Updates
From this location you can uninstall any updates that you are having problems with. The trick here is to know which update you are looking for that is causing you a problem. This may be identified by either the Windows Update Log (see above), Windows Event Viewer, personal observation or other knowledge base searches.
This article has discussed various ways of troubleshooting Windows Update problems and how to resolve them.